Table of content
1. Introduction
CSS modules are just like plain CSS which you already know with lots of extra advantages and some specific rules.
2. Why we are using CSS modules and what is the need to use them?
If you have worked in ReactJS for creating your web apps, then you might be aware that all of the CSS files in your application are combined and get added to the style tag of your document (at the top).
Due to this, the styles of the classes get overridden and you may get some styling issues in the application.
NOTE: The overridden depends on the import of the component and most last import will override the previous ones.
Example, let's say we have two components folder
ComponentOne
index.js
style.css
ComponentTwo
index.js
style.css
and we have h1 tag with classname heading, h2 tag with classname sub-heading in both ComponentOne & ComponentTwo.
ComponentOne.js
import "./style.css";
export default CompOne = () => {
return (
<>
<h1 className="heading">Component One Heading--green</h1>
<h2 className="sub-heading">Component One Subheading--yellow</h2>
</>
);
};
ComponentTwo.js
import "./style.css";
export default CompTwo = () => {
return (
<>
<h1 className="heading">Component Two Heading--red</h1>
<h2 className="sub-heading">Component Two Subheading--blue</h2>
</>
);
};
We have given color styles to both tags in their respective style.css file and import them in their respective component file.
in ComponentOne > style.css
.heading {
color: green;
}
.sub-heading {
color: yellow;
}
in ComponentTwo > style.css
.heading {
color: red;
}
.sub-heading {
color: blue;
}
and we are importing both the components in App.js
import ComponentOne from "./ComponentOne";
import ComponentTwo from "./ComponentTwo";
import "./styles.css";
export default function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<ComponentOne />
<ComponentTwo />
</div>
);
}
Please take note that we have imported ComponentTwo after importing ComponentOne and below is the output
What happened here is that the ComponentTwo style.css has taken priority and its style has overridden the style of ComponentOne folder's style.css.
What if we import ComponentTwo before ComponentOne?
Have you noticed the difference? What happened here is the ComponentOne style.css has taken priority and its style has overridden the style of ComponentTwo folder's style.css.
And that's the biggest issue when multiple developers work on the same project and are giving the same classname to the elements.
This is one of the main reasons we should use CSS Module in ReactJS.
No one wants to clutter their code with !important overrides in CSS as it creates a lot of confusion while debugging. However, !important becomes tempting as the project grows and multiple developers work in a team. CSS Modules are one way to solve this issue.
3. How to use CSS Module in RectJS
- Instead of creating the file as
filename.cssyou have to create the file asfilename.module.css
style.module.css
.header{
font-weight:700;
color:red;
}
#sub-heading{
color: black;
background-color:white
}
- We have to then import these
CSS Modulestyles into a variable and that variable (let's say styles) will be a JavaScript object containing all the styles (classes, ids).
import styles from './style.module.css
- Then wherever you are writing your
classNamesyou have to write them like
<h1 className={styles.heading}>Heading</h1> //adding className
<h2 id={styles["sub-heading"]}>Sub Heading</h2> //adding id
We can also destructure the class names and id names.
import {heading, "sub-heading" as subheading} from './style.module.css'
// or
let { heading, "sub-heading": subheading } = styles;
Do you know why we have assigned new names to the "sub-heading" key ? check out here
NOTE: All the rules for accessing classes/ids from CSS Module will be similar to accessing keys in JS objects. As we know that the id's should be unique in the html document, whenever we give styling to the id it will get applied to that element but in CSS Module compiler used to generate a unique name for all the classes and id's defined in the CSS Module and hence the same
idname in multiple CSS Module files get different name during build time.
That's it, you are done. CSS Module is as simple as CSS is.
Let's see some of the important points of CSS Module (how to...).
4. How to write multiple class names to an element when we are using CSS Module
we can use the JSX syntax to write that
<div className={`${styles.heading} ${styles.mainHeading}`}>Heading</div> //adding multiple className
// OR
<div className={styles.heading +" "+ styles.mainHeading}>Heading</div> //adding multiple className
// not preferable
5. How can we make a global styling in CSS Module
We just need to add :global suffix before the defined classname in the CSS Module.
Syntax
:global (.myclass) {
background-color: red;
}
Example:
:global .global-style {
color:cyan
}
<h3 className="global-style">Component Heading</h3>
6. We should not give styling to the elements in CSS Module.
We should never apply CSS to an HTML element in the CSS Module because if we do so, then it will become the global one automatically.
h3 {
font-size: 20px;
font-style: italic;
}
Best practice is to create some global css file (let's say global.css) file and define all your global styling in that file.
7. Composing multiple styles together in CSS Module.
You can create a class and then compose it within other classes by using the composes selector.
.heading {
background-color: green;
color: white;
}
.main-heading {
composes: heading;
color: blue;
}
The classes being composed do not have to be in the same file. It can be imported in from another css file or module as well.
.main-heading {
composes: heading from './style.css';
color: blue;
}
8. How to define CSS variables in CSS Modules.
CSS Modules have a variable system that allows you to create variables in the CSS Module.
@value blue: #ff0000;
@value red:#0c77f8;
@value green: #aaf200;
/* Note that we have given some red kind of color code in blue variable */
.heading {
color: blue;
}
In the example above, we've created valriable blue, red and green. For cleaner referencing and reusability, these values can be defined in a separate file and then we can imported from there.
colors.css
@value blue: #ff0000;
@value red:#0c77f8;
@value green: #aaf200;
style.module.css
/* importing variable. */
@import colors: "./colors.css";
@import blue, red, green from colors;
.heading {
color: blue;
}
NOTE: in some of the documents you may see
@valuein place of@import. Both are fine, it depends on the compiler.
Please checkout the codesandbox for the css module example
9. How CSS Module works behind the scene
CSS Modules create a unique classname of the format [filename]_[classname]__[hash].
When we import our CSS Module, CSS module export the classnames and ids defined in the file like a normal JavaScript object, where the keys will be the original classnames/ids (only name) and their value will be the globally generated classes and ids (generated by webpack or any other compiler in the format mentioned above)
The build tools transform our class names into variables that are exported separately as named exports and as an object.
Although CSS Module is written like plain CSS, it actually compiles to a low-level interchangeable format called ICSS (Interoperable CSS) that is designed for loader implementers, not end-users. It is a superset of standard CSS and a low-level file format that enhances CSS.
Tools such as Webpack are used to perform this compilation process.
Also, if you import the CSS file into a different component, the key names would also be different as its locally scoped and the compiler would be named in the format of [filename]_[classname]__[hash]
You may have some questions in your mind that how it is getting exported from filename.module.css It's as simple as exporting object from JavaScript.
This image speaks 1000's of word.
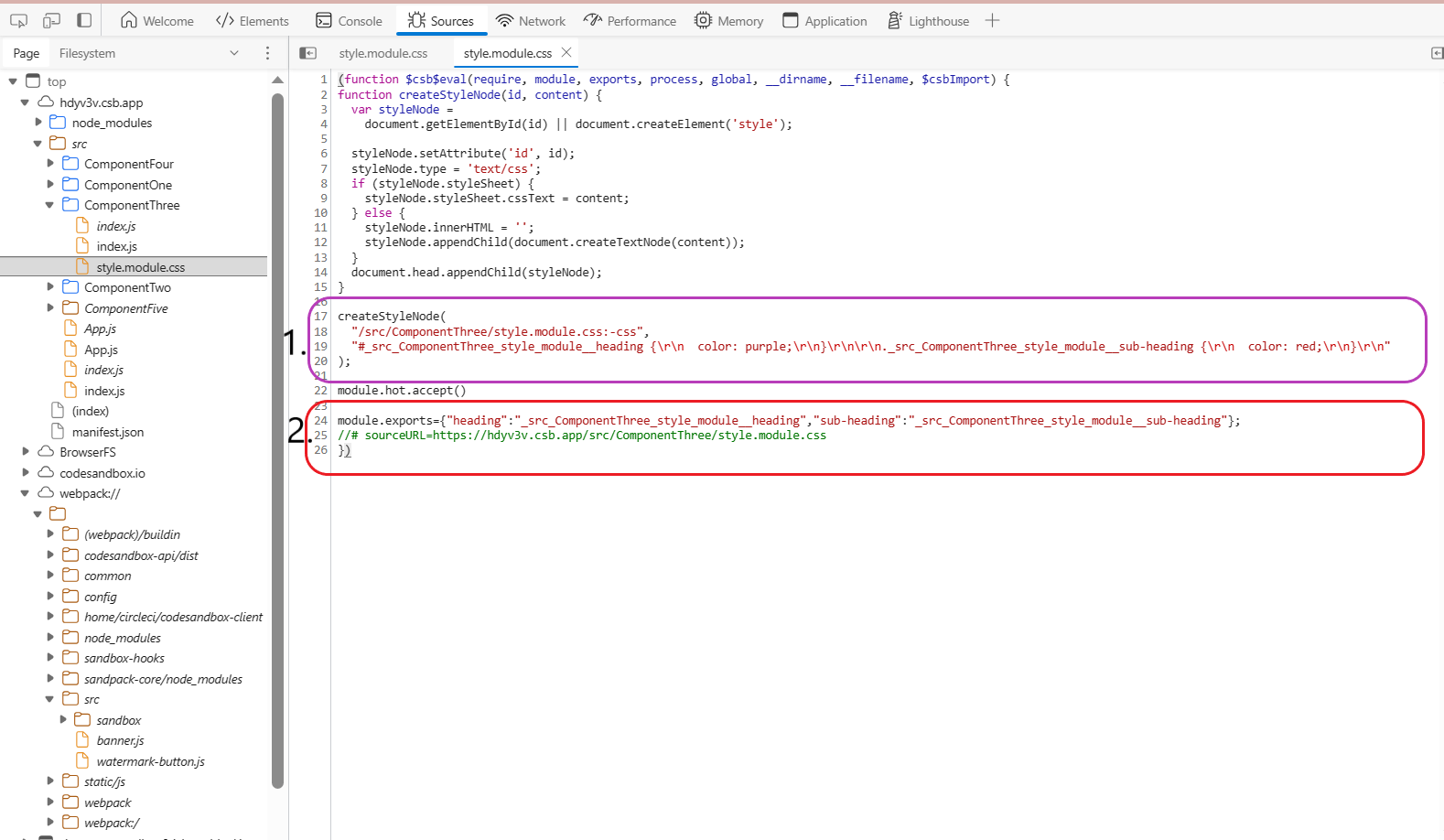
Please double-check the point 1. and point 2. marked in the image.
if you want to check the demo of how css module does the export of styles, do cehckout
10. Conclusion
Awesome! Now you become an expert in using CSS Modules in your application. CSS module are very much useful when you dont want to install any 3rd party library like StylesComponent, Emotions etc. and want to continue writing your CSS in the tradtional way. Its developer friendly, less time consuming, easy to debug and easy to manage as well.
Thank you for reading this far. This is a brief introduction of CSS Module.
If you find this article useful, share this article. Someone could find it useful too. If you find anything technically inaccurate please feel free to create a issue.
Hope it's a nice and informative read for you. VISIT https://www.capscode.in/blog TO LEARN MORE...
Few of the trending articles,
Thanks,
CapsCode
